Protecting Your Team: A Guide to Commercial Lone Worker Safety
Ensure the safety of your employees who work alone. Learn about commercial lone worker safety risks, best practices, and how Aware360 can help.
Learn how OSHA working alone laws protect workers—covering employer responsibilities, employee rights, risk assessments, and safety policies.
Prioritizing the well-being and safety of individuals is inherent to human nature. Whether they are friends, family members, or employees, their welfare should always take precedence, irrespective of legal obligations.
Nonetheless, there are instances where businesses may not prioritize this fundamental responsibility, leading to unfortunate incidents in the absence of professional guidance and oversight. This is where the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) steps in, applying its authority to enforce regulations that safeguard workers across various industries.
As an employer, comprehending and building processes to comply with OSHA laws about working alone can set a safe workplace apart from a potentially hazardous one.

By familiarizing yourself with the specific laws pertaining to employees working alone, you can proactively identify risks and implement effective safety measures. This proactive approach not only ensures the well-being of your workforce but also helps protect your company from negative consequences.
Throughout this guide, we will delve into various aspects of OSHA laws about working alone. Discover how you can ensure the safety of your employees, regardless of their working conditions. Together, we can pave the way toward a safer and more productive future.
OSHA laws about working alone play a crucial role in protecting the well-being of employees. But what exactly does it mean to work alone according to OSHA regulations? Working alone refers to situations where employees perform their tasks or duties without direct or immediate supervision or assistance.
Take, for instance, the linemen and electricians who diligently restore powerlines in remote locations, the compassionate homecare professionals who tirelessly attend to individuals unable to leave their homes, and the dedicated paramedics who swiftly navigate from one emergency situation to another.
Working alone carries inherent risks and challenges that need to be carefully managed. Any employee can face potential hazards, such as accidents, injuries, or medical emergencies, but without others nearby to hear or assist, they may go unnoticed or be assisted for prolonged periods, resulting in worst-case scenarios.
To ensure the safety of employees working alone, you must establish comprehensive safety protocols and procedures. This may involve implementing safety policies, providing training on emergency response, and equipping employees with appropriate safety solutions.
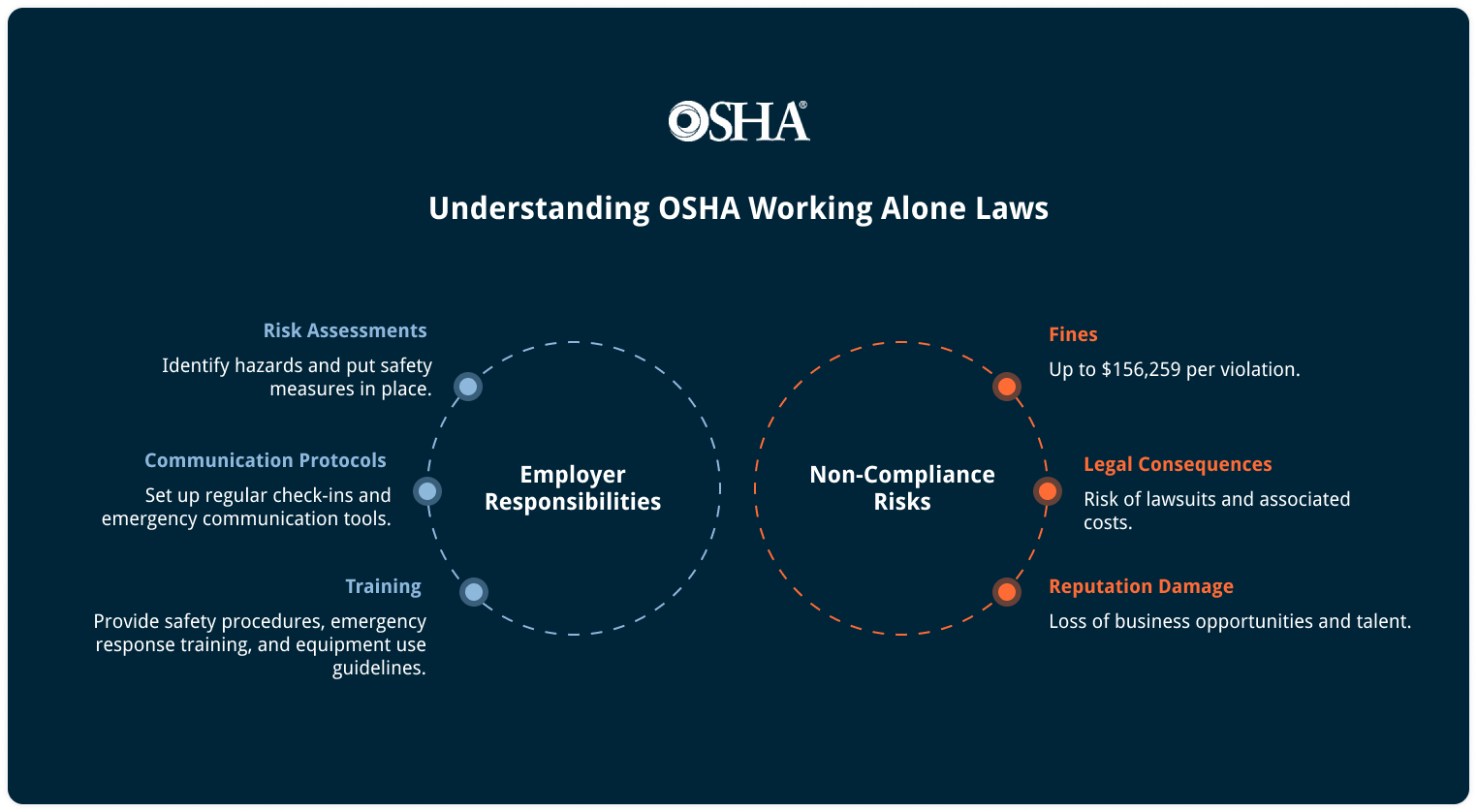
When it comes to ensuring workplace safety, OSHA laws about working alone encompass several necessary regulations that employers must understand and follow. These regulations aim to protect lone workers from potential hazards and promote a safe working environment:

Based on these guidelines, you have a responsibility to consistently monitor the well-being of your lone employees through observation or verbal communication. To effectively ensure the well-being of lone employees, it is important to establish check-in schedules, develop comprehensive safety policies, and adopt relevant safety solutions.
In the case of lone workers who operate in settings prone to unforeseen hazards, you can comply with this by consistently communicating with your employees, establishing user-friendly reporting and communication protocols, and regularly revising risk assessments and policies pertaining to lone workers to account for emerging and evolving hazards.
It is crucial to recognize that the specific regulations pertaining to working alone may vary depending on the nature of the industry and the tasks being performed. Therefore, conducting a comprehensive risk assessment and consulting relevant OSHA guidelines specific to the industry is essential.

Conducting thorough lone worker risk assessments is a critical step in ensuring the safety and well-being of your employees. A risk assessment is often defined as a systematic evaluation of the potential hazards and risks associated with solitary work, aiming to identify and mitigate any dangers that could compromise the lone worker's safety.
Based on a report from the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2021, it was revealed that there are approximately two million deaths related to work annually on a global scale. Additionally, there have been reports of half a billion cases of nonfatal injuries and illnesses caused by occupational hazards. Even more shocking is that the majority of these incidents are avoidable and could be averted through the implementation of effective control measures such as a risk assessment.
So how is it done? To begin, it is a good idea to gather a team of knowledgeable individuals, including lone workers themselves, supervisors, and safety professionals. Once you have this range of input, follow these steps:
Drafting any form of internal documentation should prioritize clarity and simplicity. Although this process can be time-consuming, the importance of this policy is immeasurable.
Adhering to OSHA guidelines helps you mitigate risks, protect lone workers, and reduce legal exposure. By implementing tailored safety measures for lone workers and staying updated on OSHA regulations and best practices, you invest in workplace safety, which in turn enhances productivity and reputation through a culture of safety.
By adopting Aware360's SafetyAware lone and at-risk worker safety solution, you experience the power of advanced technologies and innovative features. Our comprehensive solution set includes a range of safety devices, all boasting a host of people-first capabilities. By investing in our solutions, you not only adhere to the latest safety rules and regulations but also prioritize the well-being of your lone workers leveraging the most effective solutions on the market.
Take the first step towards creating a safer working environment for all by booking a meeting with us. Together, we can save lives.
Employers must ensure that lone employees are regularly accounted for by sight or verbal communication. The General Duty Clause requires employers to make a reasonable effort to ensure that all employees, including those working alone, do not encounter workplace hazards.
To ensure compliance, employers should carry out the following steps:
Ensure the safety of your employees who work alone. Learn about commercial lone worker safety risks, best practices, and how Aware360 can help.
Explore our ultimate guide on lone worker safety, covering risk assessments, legislation, policies, and strategies to protect employees.
It’s estimated that 25 million workers work alone across North America. Answer these four questions to identify if your employees are one of them.